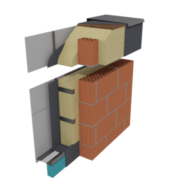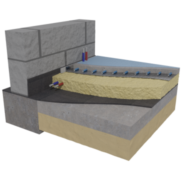
PUR foam insulation
Spray insulation serves to insulate buildings; it is quite different from traditional insulation. This is both the latest and also the most accurate way to stop heat transfer through walls, roof and other building partitions.
Explore the Purios range of spray insulation products.